Difference between revisions of "Shortest Path"
m (Fixed Link) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
The algorithm functions as follows: | The algorithm functions as follows: | ||
# The first node has a distance of 0, this is locked in and labeled node one. | # The first node has a distance of 0, this is locked in and labeled node one. | ||
| − | # Each | + | # Each unlocked node that is connected directly to a locked node by a weighted arc is given a temporary label, equal to the total weight to reach it (from the starting node) if the new distance is less then any previously marked. |
| − | # The | + | # The node closest to the start is locked in with the shortest distance available and marked as the next node in the path. |
| − | # | + | # The previous 2 steps are repeated: the distance to the each unlocked node connected to a locked node is noted and the closest node to the start is selected (regardless of when the distance was given). |
# Once every node is marked, the shortest path would be the backwards path from the last node, where taking the arc reaches the distance on the locked in node until the final number is zero at the start. | # Once every node is marked, the shortest path would be the backwards path from the last node, where taking the arc reaches the distance on the locked in node until the final number is zero at the start. | ||
| + | [[File:Dijkstra.png|thumb]] | ||
Revision as of 12:08, 22 May 2017
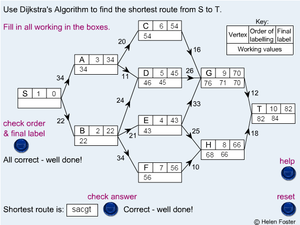
The shortest path is usually found by Dijkstra's algorithm. The algorithm functions as follows:
- The first node has a distance of 0, this is locked in and labeled node one.
- Each unlocked node that is connected directly to a locked node by a weighted arc is given a temporary label, equal to the total weight to reach it (from the starting node) if the new distance is less then any previously marked.
- The node closest to the start is locked in with the shortest distance available and marked as the next node in the path.
- The previous 2 steps are repeated: the distance to the each unlocked node connected to a locked node is noted and the closest node to the start is selected (regardless of when the distance was given).
- Once every node is marked, the shortest path would be the backwards path from the last node, where taking the arc reaches the distance on the locked in node until the final number is zero at the start.