Graphs
Contents
What is a graph
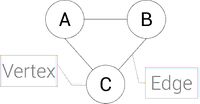
A graph is an abstract data structure. It can be used to solve routine problems.
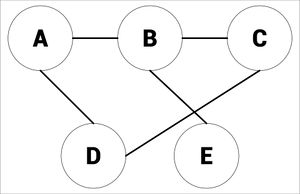
Vertices connected by an edge (see picture) are called Neighbours.
The degree of a vertex is how many things are connected to it, in the picture below, there would be 2:
Edges can also be called connectors and vertex can also be called nodes or entries.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PMPMDZqeipw&list=PLCiOXwirraUD0G290WrVKpVYd3leGRRMW&index=7
Terms
weighted graph
Each edge/arc has an associated value, which can be used for distance, cost and so on.
vertex/node
An entity, location within the graph (represented by a circle).
edge/arc
A connection between two vertex/nodes
undirected graph
You can travel either direction on an edge/arc. For example an edge between A & B allows movement from A to B and from B to A.
directed graph
Each edge/arc will have an arrow to indicate the direction of travel. This will require additional edges to cover both directions.
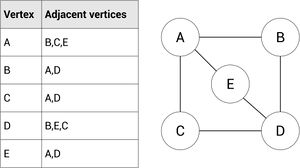
Adjacency List
An adjacency matrix is a list showing the what vertexes are connected to their neighbors. This is represented by a list showing what vertex is connected to the other.
Adjacency Matrix
This is a list shown in binary for the values that are going to be connected. It usually helps to transfer the matrices into a list first before you turn it into a graph to make things easier.
Comparison of List VS Matrix
| List | Matrix |
|---|---|
| for a node you need to look at all nodes it is connected to | Its quicker to find an edge |
| Less space, no wastage | Stores information about each edge |