Encryption
This section needs expansion.
You can help by adding to it.
Contents
Definitions
Plain text - The data in human readable form.
Cipher - An encryption method or algorithm.
Key - The data used to encrypt or decrypt the plain text.
Cipher text - The encrypted data which can only be understood if decrypted.
Caesar Cipher
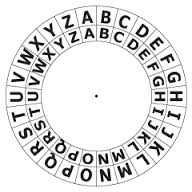
The creator was Julius Caesar. It is a substitution cipher which works by shifting letters by a number. The easiest way to look at a caesar cipher is to think of an inner and outer wheel, each wheel has the letters of the alphabet on its edge. When the letter A on both wheels are aligned the shift is 0 as in the image below:
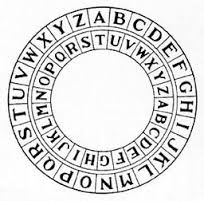
The shift turns the inner wheel a specific number of spaces. The image below shows a shift of 7:
Issues with Caesar Cipher
- There are only 25 possible keys, 26 makes the same output as the input so is just like a shift of 0. Any shift above 26, eg 45 will create an identical output as one of the shifts between 1 & 25.
- This cipher only encrypts letters so the letter spacing pattern will be identical to the plain text. You can therefore select an encrypted block of text and know it has a meaning. With brute force you could discover the exact shift (ie one shift will make a recognisable word).
- The key is constant throughout the text, so if you crack one word you crack the entire cipher text.
- With sufficient cipher text you could count the frequency of every letter used. The most frequent is likely to be the character for 'e', you can then calculate the shift.
Alternative Substitution Cipher
The caesar cipher is a very basic substitution cipher. A more secure method would be to generate a random alphabet (including a space) which could then be used with the standard alphabet to map from an existing character to the new character: File:Subcipher.jpg