Difference between revisions of "BNF - Syntax Diagrams"
(→BNF) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | ==overview== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <youtube>https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x1gGInKNCRw&list=PLCiOXwirraUAnbNTfWFxkoq5MoIair49B&index=6</youtube> | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x1gGInKNCRw&list=PLCiOXwirraUAnbNTfWFxkoq5MoIair49B&index=6 | ||
| + | |||
==BNF== | ==BNF== | ||
Backus Naur Form is a way of describing the syntax of a value to form a new value. <br /> | Backus Naur Form is a way of describing the syntax of a value to form a new value. <br /> | ||
Revision as of 13:18, 11 June 2018
Contents
overview
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x1gGInKNCRw&list=PLCiOXwirraUAnbNTfWFxkoq5MoIair49B&index=6
BNF
Backus Naur Form is a way of describing the syntax of a value to form a new value.
For example:
<digit> ::= 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
This declares that <digit> can only be the numbers 0-9, specifically 0 OR 1 OR 2 OR 3 etc.
This notation can also be recursive:
<integer> ::= <digit> | <digit><integer>
This states that an integer can be a digit or a digit followed by another integer.
Quiz
To see if you remember what you have learned about BNF, take this quick test either by yourself, or with friends: https://play.kahoot.it/#/?quizId=cad3ec51-29de-45d6-968d-6a95958553f2
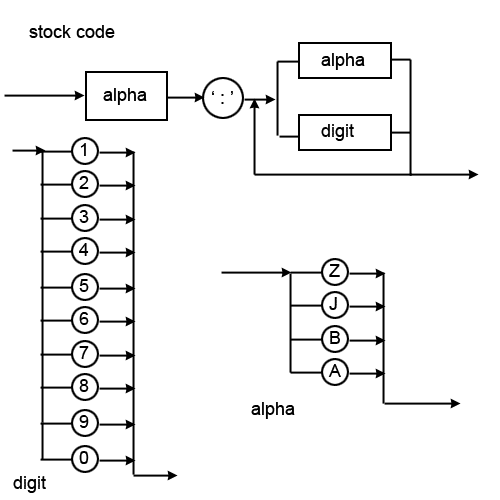
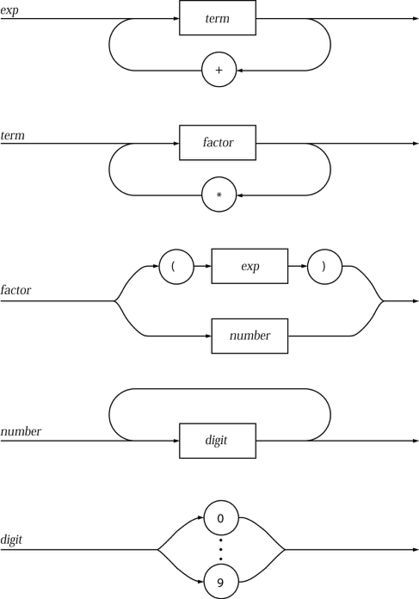
Syntax Diagrams
These are a diagram approach similar to BNF, they also describe the syntax allowed.
A recursive example: