Difference between revisions of "Flip Flops"
(→What is a flip flop) |
(→Problems with basic (SR) flip flops) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
==Problems with basic (SR) flip flops== | ==Problems with basic (SR) flip flops== | ||
| + | The downside of the SR Flip Flop is that if both Reset & Set are switched both Q and Not Q are on, which is not allowed. Also if both Reset & Set are changed at the same time from on to off (ie both on to both off) we cannot guarantee the output produced for Q. | ||
==D and T type Flip Flops== | ==D and T type Flip Flops== | ||
Revision as of 17:22, 22 May 2017
Contents
What is a flip flop
A flip-flop is used to store binary data, and is a simple latching circuit. When a value is set on the flip flop, the value is retained even when the input is switched off. This is how you can store a single bit of data in a computers memory.
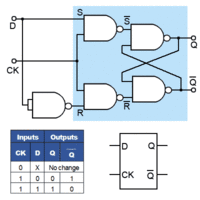
Basic (SR) Flip Flops
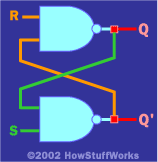
Basic flip flops are created using two NAND gates cross couples as seen in the image.
Problems with basic (SR) flip flops
The downside of the SR Flip Flop is that if both Reset & Set are switched both Q and Not Q are on, which is not allowed. Also if both Reset & Set are changed at the same time from on to off (ie both on to both off) we cannot guarantee the output produced for Q.
D and T type Flip Flops
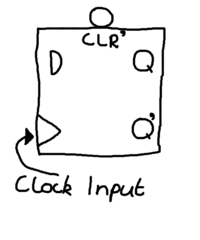
A flip flop has two inputs. One input is a control input. For a D flip flop, the control input is labelled D. For a T flip flop, the control input is labelled T. The other input is a clock input, labelled either with a triangle or CK. When a clock is drawn with a triangle like the ones below, these represent a positive-edge triggered clock, meaning that these can only change state when the clocks cycle is on a positive value i.e 1. When the clock is not on a positive value the bit stored within the flip flop is held i.e doesn't change.
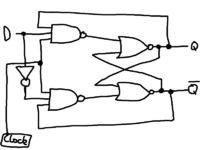 200px Logic circuit for a T-Flip Flop
200px Logic circuit for a T-Flip Flop