Difference between revisions of "Multiplication"
(→Revision) |
(→TRC PowerPoint) |
||
| (24 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | =Overview= | ||
| + | Video from 5:46 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <youtube>https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t15dhDG_WUA&list=PLCiOXwirraUDGCeSoEPSN-e2o9exXdOka&index=2</youtube> | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t15dhDG_WUA&list=PLCiOXwirraUDGCeSoEPSN-e2o9exXdOka&index=2 (5:46 - End) | ||
| + | |||
=Binary Multiplication= | =Binary Multiplication= | ||
Binary Multiplication uses a combination of multiplying by one, shifting and addition. When multiplying a binary number by 10 it is simply shifted to the left into the next column, this multiplies the original number by 2. Multiplying by 100 causes a shift of two places to the left which multiplies the original number by four. | Binary Multiplication uses a combination of multiplying by one, shifting and addition. When multiplying a binary number by 10 it is simply shifted to the left into the next column, this multiplies the original number by 2. Multiplying by 100 causes a shift of two places to the left which multiplies the original number by four. | ||
| Line 7: | Line 14: | ||
For every 0 in the multiplier nothing is written. | For every 0 in the multiplier nothing is written. | ||
| − | For example multiply 22 by 5, which in binary is 10110 by 101 | + | For example multiply 22 by 5, which in binary is 10110 by 101: |
| + | |||
| + | 10110 | ||
| + | x 101 (Multiplier) | ||
starting from right to left there is a 1 in the multiplier so we write the number being multiplied normally 10110. | starting from right to left there is a 1 in the multiplier so we write the number being multiplied normally 10110. | ||
| + | 10110 | ||
| + | x 101 (Multiplier) | ||
| + | ----- | ||
| + | 10110 | ||
The second number in the multiplier is a 0 so we write nothing. | The second number in the multiplier is a 0 so we write nothing. | ||
The last number in the multiplier is a 1 and there are two digits before it a 0 and a 1, 2 digits, so we write out the number being multiplied with 2 zeros to the right of it, 10110'''00''' | The last number in the multiplier is a 1 and there are two digits before it a 0 and a 1, 2 digits, so we write out the number being multiplied with 2 zeros to the right of it, 10110'''00''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | 10110 | ||
| + | x 101 (Multiplier) | ||
| + | ------- | ||
| + | 10110 | ||
| + | 1011000 | ||
| + | ------- | ||
After the number has been multiplied by all the digits in the multiplier we simply add them up using binary addition, be careful when writing the numbers out so they are lined up correctly for addition. | After the number has been multiplied by all the digits in the multiplier we simply add them up using binary addition, be careful when writing the numbers out so they are lined up correctly for addition. | ||
| − | + | 10110 + | |
1011000 | 1011000 | ||
| − | + | ------- | |
| + | 1101110 | ||
| + | ------- | ||
| + | |||
| + | Converting 1101110 to denary gives us 110, which is 22x5. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Binary 1.jpg|500px]] | ||
| + | [[File:Binary 2.jpg|250px]] | ||
| + | [[File:Binary 3.jpg|240px]] | ||
=Revision= | =Revision= | ||
| Line 49: | Line 79: | ||
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
Multiply 10111 by 101. Leave your answer as an 8-bit binary number. | Multiply 10111 by 101. Leave your answer as an 8-bit binary number. | ||
| − | { | + | { 1110011 } |
{ | { | ||
| Line 71: | Line 101: | ||
-100100 | -100100 | ||
|| You added them together | || You added them together | ||
| − | + | + | +100010011 |
|| Correct | || Correct | ||
-1100100 | -1100100 | ||
| Line 88: | Line 118: | ||
|| 10100101 | || 10100101 | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | Multiply 1011001 by 1101. Leave your answer as an 8-bit binary number. | ||
| + | { 10010000101 } | ||
| + | |||
| + | {What is 110100 x 1101? | ||
| + | | type="()" } | ||
| + | |||
| + | +101010100 | ||
| + | ||Correct. | ||
| + | -100001010 | ||
| + | ||You added them together. | ||
| + | -101010010 | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | Multiply 1010011 by 101. Leave your answer as an 8-bit binary number. | ||
| + | { 110011111 } | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | Multiply 11011 by 110. Leave your answer as an 8-bit binary number. | ||
| + | { 101100010 } | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | Multiply 01101 by 11. Leave your answer as an 8-bit binary number. | ||
| + | { 00100111 } | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | Multiply 101010 by 111. Leave your answer as a binary number. | ||
| + | { 100100110 } | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | Multiply 11111 by 11. Leave your answer as an 8-bit binary number. | ||
| + | { 01011101 } | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | Multiply 110011 by 101. Leave your answer as an 8-bit binary number. | ||
| + | { 111111111 } | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | Multiply 00110101 by 1111. Leave your answer as an 8-bit binary number. | ||
| + | { 1100011011 } | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | Multiply 1111 by 1111. Leave your answer as an 8-bit binary number. | ||
| + | { 11100001 } | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | Multiply 11111101 by 1101. Leave your answer as an 8-bit binary number. | ||
| + | { 110011011001 } | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | Multiply 11100011 by 1011. Leave your answer as an 8-bit binary number. | ||
| + | { 100111000001 } | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | Multiply 10001111 by 111. Leave your answer as an 8-bit binary number. | ||
| + | { 1111101001 } | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | Multiply 11100111 by 11. Leave your answer as an 8-bit binary number. | ||
| + | { 1010110101 } | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
Latest revision as of 09:24, 25 September 2020
Overview
Video from 5:46
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t15dhDG_WUA&list=PLCiOXwirraUDGCeSoEPSN-e2o9exXdOka&index=2 (5:46 - End)
Binary Multiplication
Binary Multiplication uses a combination of multiplying by one, shifting and addition. When multiplying a binary number by 10 it is simply shifted to the left into the next column, this multiplies the original number by 2. Multiplying by 100 causes a shift of two places to the left which multiplies the original number by four.
The rules for multiplying a binary number by another binary number is:
For every 1 in the multiplier repeat the number being multiplied with as many zero's to the right of it as there are digits before the 1 in the multiplier. For every 0 in the multiplier nothing is written.
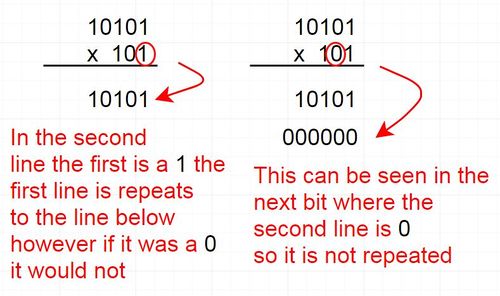
For example multiply 22 by 5, which in binary is 10110 by 101:
10110 x 101 (Multiplier)
starting from right to left there is a 1 in the multiplier so we write the number being multiplied normally 10110.
10110 x 101 (Multiplier) ----- 10110
The second number in the multiplier is a 0 so we write nothing.
The last number in the multiplier is a 1 and there are two digits before it a 0 and a 1, 2 digits, so we write out the number being multiplied with 2 zeros to the right of it, 1011000
10110 x 101 (Multiplier) ------- 10110 1011000 -------
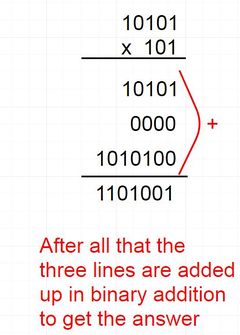
After the number has been multiplied by all the digits in the multiplier we simply add them up using binary addition, be careful when writing the numbers out so they are lined up correctly for addition.
10110 + 1011000 ------- 1101110 -------
Converting 1101110 to denary gives us 110, which is 22x5.