Difference between revisions of "C++ Drawing to the screen"
(Created page with "=Using Graphics.h= There are many libraries for drawing graphics to the screen, these examples will show the standard 'Graphics.h' approach. You can the required files from: [...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | = | + | =SFML= |
| − | + | This method will require you to install some packages. In Visual Studio, and Project, select 'Manage Nuget Packages'. | |
| + | |||
| + | Click the browse tab and type: | ||
| + | |||
| + | 'sfml' | ||
| + | |||
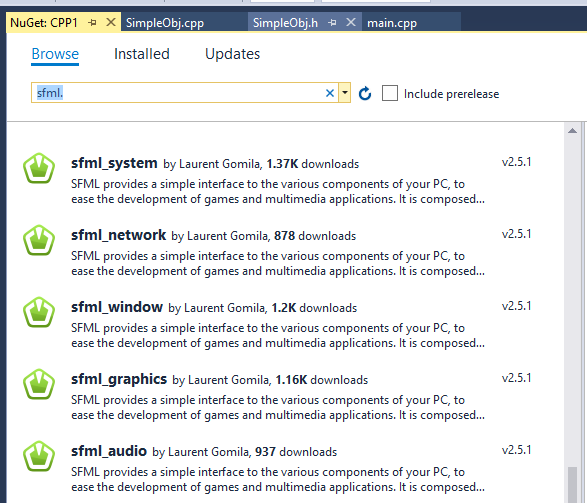
| + | Now look for the version numbers, each version has a slightly different name. I have found: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Sfml.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | SFML has 5 different components, so click each one and click install. | ||
==Drawing a Line== | ==Drawing a Line== | ||
Revision as of 14:15, 13 June 2019
SFML
This method will require you to install some packages. In Visual Studio, and Project, select 'Manage Nuget Packages'.
Click the browse tab and type:
'sfml'
Now look for the version numbers, each version has a slightly different name. I have found:
SFML has 5 different components, so click each one and click install.
Drawing a Line
// C++ Implementation for drawing line
- include <graphics.h>
- include <winbgim.h>
// driver code int main() {
// gm is Graphics mode which is a computer display // mode that generates image using pixels. // DETECT is a macro defined in "graphics.h" header file int gd = DETECT, gm; // initgraph initializes the graphics system // by loading a graphics driver from disk initgraph(&gd, &gm, ""); // line for x1, y1, x2, y2 line(150, 150, 450, 150); getch(); // closegraph function closes the graphics // mode and deallocates all memory allocated // by graphics system . closegraph();
}